In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, understanding the pivotal role of a datacenter is crucial for IT professionals aiming to optimize operational efficiency and bolster reliability. As businesses increasingly rely on digital solutions, a comprehensive grasp of data center services and their impact becomes indispensable. From exploring advanced infrastructures to assessing the benefits of a colocation data center, it's essential to discern how these facilities support the backbone of our interconnected world. Additionally, knowing the crucial components of data center infrastructure and the tier levels that define their reliability helps in making informed decisions. This post will navigate you through these critical aspects, empowering you to choose a data center that aligns perfectly with your professional needs and enterprise goals.
Defining Data Center and Its Importance
In the digital age, where data drives decision-making and supports critical operations, the concept of a data center becomes paramount. These centralized facilities house the computing infrastructure necessary to store, process, and disseminate data across various networks. Data center services form the backbone for businesses looking to handle data reliably and efficiently. But what exactly defines a data center?
A data center infrastructure typically includes:
- Servers: Physical or virtual machines that host applications and store data.
- Network Equipment: Routers, switches, and firewalls manage data flow and security.
- Storage Systems: Devices for storing large volumes of data consistently.
The primary role of a colocation data center is to provide space and power to businesses, allowing them to house their hardware within a shared facility. This solution is especially beneficial for companies seeking to minimize expenses and optimize performance without investing heavily in their own facilities.
The importance of data centers extends beyond just providing service uptime and operational flexibility. They are integral to enhancing the following:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced capital expenditure by leveraging shared resources. |
| Security | Robust physical and cyber protection measures. |
| Scalability | Easy to expand capacity as business demands grow. |
| Reliability | Enhanced uptime with backup systems, thereby minimizing potential outages. |
In today’s competitive landscape, IT professionals must recognize the critical role data centers play in ensuring business continuity and competitive advantage. By understanding both the functions and advantages of data centers, organizations can effectively harness technology's potential to fuel growth and innovation. This foundation leads to exploring how varying tier levels further influence operational reliability and service quality.

Understanding Data Center Services
Navigating the world of Data center services is crucial for IT professionals aiming to optimize performance and efficiency. These services are essential for businesses that require robust IT infrastructure, scalable resources, and reliable uptime. Here's a closer look at what these services entail:
- Managed Services:
- IT infrastructure management
- Security and monitoring
- Backup and disaster recovery
- Colocation Services:
- Utilization of colocation data center facilities
- Physical space, power, and cooling provided
- Shared resources for cost efficiency
- Cloud Services:
- Virtual servers and storage
- Flexible, on-demand scaling
- Integrated with global networks
- Connectivity Services:
- High-speed internet connections
- Redundant network paths
- Access to multiple service providers
Each of these services plays a pivotal role in enhancing the performance of IT operations. A colocation data center, for example, provides businesses with the infrastructure necessary to house their servers while reducing the burden of managing physical facilities. Additionally, managed services offer comprehensive support, ensuring that IT systems run smoothly without requiring the constant attention of in-house teams.
Services like cloud and connectivity further enable businesses to expand their reach swiftly and securely. Cloud services allow IT professionals to leverage scalable resources without the need for significant capital investment. Meanwhile, connectivity services guarantee seamless communication and data exchange, vital for businesses with global operations.
For IT professionals, understanding and implementing these data center services is key to building resilient and future-proof IT systems. By selecting the appropriate blend of services, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve their ability to adapt to evolving technological landscapes. This strategic approach ensures that the data center infrastructure remains reliable, efficient, and scalable for future demands.
Exploring Colocation Data Centers
In the landscape of modern IT infrastructure, Colocation Data Centers play a pivotal role for organizations seeking flexibility and efficiency. Essentially, these facilities allow businesses to rent space for their servers and other computing hardware within a professional data center. This arrangement offers numerous advantages, especially for companies that do not wish to maintain their own on-premises server rooms.
Understanding the Benefits
Colocation Data Centers bring a wealth of benefits to the table:
- Cost Efficiency: By sharing space and resources, businesses can significantly reduce the costs associated with maintaining physical infrastructure.
- Scalability: Companies can easily scale their operations up or down as needed, without worrying about space constraints or hardware limitations.
- Reliability: These centers provide robust Data center infrastructure, including uninterrupted power supplies, advanced cooling systems, and enhanced security measures, ensuring high availability.
- Connectivity Options: They offer multiple, carrier-neutral connectivity options to ensure optimal network performance and redundancy.
Security and Compliance
Security is a critical concern when housing sensitive data and applications. Colocation Data Centers adhere to industry regulations and standards, such as ISO and SOC certifications, to ensure data protection and compliance. Enhanced physical security measures, such as biometric access controls and 24/7 surveillance, are standard features.
Comparing Colocation with Other Data Center Services
| Feature | Colocation | Cloud | On-Premises |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control over Data | High | Low | Full |
| Scalability | Moderate to High | High | Limited |
| Initial Investment | Medium to Low | Low | High |
| Ongoing Costs | Medium | Variable | High |
Deciding for Your Business
For IT professionals, choosing the right Data center services is crucial for aligning with operational goals. While Colocation Data Centers offer a balance of control, cost savings, and reliability, it’s important to assess your business’s specific requirements before making a decision. Consider factors such as proximity, service level agreements, and scalability needs to find a data center solution that complements your strategic vision.
Key Components of Data Center Infrastructure
The reliability and efficiency of data center infrastructure hinge upon its meticulous design and the seamless integration of various components. Understanding these key aspects is essential for IT professionals tasked with managing and optimizing these enterprise environments. Here, we delve into the critical components that contribute to a robust and resilient infrastructure.
- Power Systems:
- Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS): Vital for providing continuous electricity during outages.
- Generators: Serve as backup power to keep critical systems operational.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): Manage and distribute the electrical load efficiently.
- Cooling Systems:
- HVAC Systems: Regulate temperature and humidity to prevent overheating.
- Chilled Water Systems: Offer efficient cooling for large operations.
- Raised Floors: Facilitate optimal airflow and cooling pathways.
- Networking Equipment:
- Routers and Switches: Facilitate data transfer and communication between internal and external networks.
- Firewalls and Security Appliances: Protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Cabling Systems: Structured cabling ensures organized and manageable network connectivity.
- Storage Solutions:
- SAN and NAS: Offer scalable and flexible storage solutions.
- Backup Systems: Ensure data recovery and protection.
- Physical Security:
- Biometric Systems and Access Controls: Prevent unauthorized physical entry.
- Surveillance Cameras: Monitor activities to deter security breaches.
The table below consolidates these components and their roles:
| Component | Functionality | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Power Systems | Provide continual power supply | Essential for uptime and reliability |
| Cooling Systems | Maintain optimal operating conditions | Prevents hardware failure and data loss due to overheating |
| Networking Equipment | Enable effective data communication and protection | Critical for seamless operations and security |
| Storage Solutions | Facilitate data storage and retrieval | Crucial for data management and backup |
| Physical Security | Ensure safety and control of data center premises | Protects against unauthorized access and physical threats |
To ensure reliable and scalable data center services using colocation data center facilities, these components must be efficiently integrated and maintained. As IT professionals prioritize various aspects of infrastructure planning, a focus on these components can significantly boost performance and reliability to meet the evolving demands of modern technology solutions.

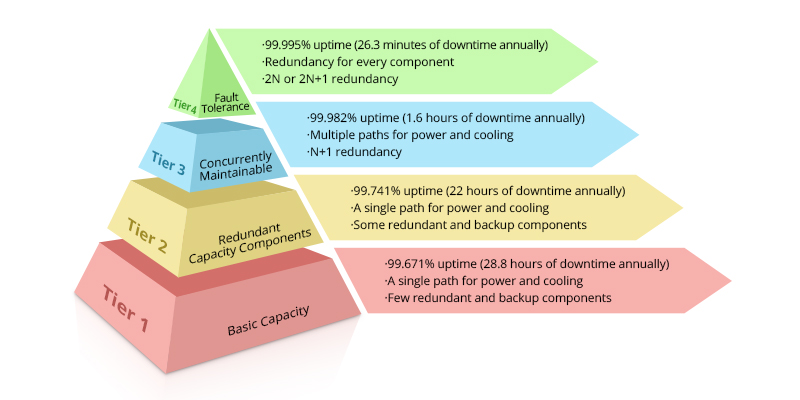
An Overview of Tier Levels in Data Centers
When it comes to ensuring the reliability and efficiency of data center services, the concept of tier levels holds a significant place. Tier levels, as defined by the Uptime Institute, categorize data centers based on their infrastructure design, capacity, and system uptime.
Here's a breakdown of the tier levels commonly used in the industry:
| Tier Level | Description | Redundancy/Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Tier I | Basic site infrastructure | Up to 99.671% availability with no redundancy |
| Tier II | Redundant capacity components | Up to 99.741% availability with partial redundancy |
| Tier III | Concurrently maintainable infrastructure | Up to 99.982% availability with N+1 redundancy |
| Tier IV | Fault-tolerant infrastructure | Up to 99.995% availability with 2N redundancy |
- Tier I, the most basic level, offers no redundant components and aims to provide a functional yet non-secure environment. It is generally suitable for small businesses with limited budgets.
- Tier II systems introduce redundant capacity components. Although there is some degree of redundancy, if availability does dip, maintenance must be scheduled, which can cause disruptions.
- Tier III is considered suitable for most businesses. Its design supports all operations, including maintenance, without requiring downtime, thanks to its N+1 redundancy model, which ensures continued operation even if one component fails.
- Tier IV represents the pinnacle of reliability in colocation data centers. This level is designed for critical enterprises that require an unyielding zero-downtime environment, thanks to its fully fault-tolerant, 2N redundancy structure.
Choosing the correct tier level for your data center infrastructure is crucial. It hinges on understanding your business needs, budget constraints, and the level of uptime required to keep operations running smoothly. Tier levels are more than just labels; they reflect the inherent reliability and tolerance for disruptions that a business is willing to invest in.
How Tier Levels Affect Data Center Reliability
Understanding tier levels is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your data operations. By design, tier levels categorize data centers based on their power, cooling, and fault-tolerant capabilities. Here's how they directly influence the reliability of a Colocation data center:
Tier Levels and Their Role
- Tier I: Basic capacity level with a single path for power and cooling distribution and no redundant components. This foundational category often experiences downtime due to scheduled maintenance, making it less reliable for critical data center services.
- Tier II: Slightly more reliable with some redundant infrastructure components. This tier reduces unforeseen outages but still suffers during maintenance or unexpected failures.
- Tier III: Offers multiple independent power and cooling paths, ensuring that equipment is accessible even during maintenance without shutting down operations. Ideal for businesses with a moderate need for continuous data center infrastructure availability.
- Tier IV: The highest level of reliability. It features fully redundant systems and a fault-tolerant setup. This arrangement ensures no disruption even under adverse conditions, making it suitable for mission-critical applications demanding the utmost uptime.
Key Impact Areas
- Downtime Reduction: Higher-tier levels significantly decrease unplanned downtime through redundancy, directly enhancing operational reliability.
- Performance Stability: When a tier level supports dual, parallel paths for power and cooling, it stabilizes operations by allowing maintenance without affecting the system's performance.
- Risk Management: Advanced tier levels provide robust setups that manage unexpected risks more effectively. In doing so, they mitigate the impact on business operations and ensure consistency.
Tables comparing downtime and the potential impact on business operations across different tiers can highlight the empirical benefits of selecting higher-tier levels for data center services.
Choosing the appropriate tier level ensures the optimal balance between cost and reliability, aligning with the specific requirements of your organization's data management needs. This understanding empowers you to make informed decisions for enhancing the resilience of your digital ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Data Center for Your Needs
Selecting the ideal Data center services for your organization's requirements involves careful consideration of several factors. Understanding these key elements will help ensure that you choose a facility that aligns perfectly with your operational and strategic goals. Here is a breakdown of critical considerations:
1. Location:
- Proximity to your main business locations can reduce latency.
- Consider areas less susceptible to natural disasters for enhanced security.
2. Tier Level:
- Evaluate the Tier levels as these dictate the reliability and redundancy of data center infrastructure.
- Higher Tier levels offer better uptime guarantees and may suit mission-critical applications.
3. Security:
- Look for advanced physical and network security measures.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
4. Connectivity:
- Check for multiple connectivity options to ensure high-speed and reliable network access.
- Consider facilities offering carrier-neutral connectivity for flexibility.
5. Scalability:
- Ensure the colocation data center can accommodate your future growth.
- Evaluate the ease of expanding space and resources.
6. Energy Efficiency:
- Opt for facilities using efficient cooling and energy practices.
- Verify the data center’s commitment to sustainable operations.
7. Cost:
- Compare costs against the level of service and infrastructure provided.
- Analyze the total cost of ownership, including potential downtime impacts.
Here's a concise table to help you weigh these factors:
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Location | Proximity and risk avoidance |
| Tier Level | Uptime and reliability |
| Security | Data protection and compliance |
| Connectivity | Network speed and flexibility |
| Scalability | Future growth accommodation |
| Energy Efficiency | Sustainable and cost-effective |
| Cost | Value versus expenditure |
By diligently assessing these criteria, IT professionals, including software developers, network engineers, and cybersecurity experts, can make informed choices that align with their specific needs and long-term business strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are data center tier levels?
Data center tier levels are a classification system defined by the Uptime Institute that categorizes data centers based on their reliability, redundancy, and performance capabilities. There are four tiers in this classification system, with Tier I being the most basic and Tier IV being the most advanced. Each level represents a higher degree of redundancy, fault tolerance, and uptime guarantees, which are crucial for ensuring continuous data center operations.
How does Tier I differ from Tier IV in a data center?
Tier I is the most basic level within the data center tier classification, providing a single, non-redundant distribution path for power and cooling, which means it offers limited protection against outages. In contrast, Tier IV data centers offer the highest level of redundancy and fault tolerance, with multiple independent and physically isolated systems, ensuring a very high uptime (99.995%). This tier is designed to support critical mission operations that cannot afford any disruptions.
Why is it important to understand data center reliability?
Understanding data center reliability is essential for businesses as it influences their ability to deliver consistent and dependable services to customers. A reliable data center ensures that critical business functions run smoothly without interruption, which is crucial for maintaining business operations, customer satisfaction, and protecting a company's reputation. Businesses that thoroughly understand data center reliability can make informed decisions about selecting appropriate data center services that align with their operational needs and risk management strategies.
What factors should be considered when evaluating data center reliability?
When evaluating data center reliability, several key factors should be considered, including infrastructure redundancy, power and cooling systems, uptime performance record, security measures, disaster recovery capabilities, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, one should consider the data center's location, network connectivity, and the expertise of the management team. Evaluating these elements helps in selecting a data center facility that can provide the necessary level of reliability to support a company's specific operational and business continuity requirements.


.png)
.png)
.png)